This Week in Biotech #004
Catch up on the latest biotech breakthroughs and upcoming trends (8/9-8/16).
Welcome to This Week in Biotech by Biotech Blueprint, your weekly dose of the latest biotech breakthroughs, clinical trial updates, pharma company news, and forecasts of what’s on the horizon.
MARKET UPDATE
In the last week, there was increased market turbulance as apparent from the VIX chart below (volatility index). This recent increased volatility in the stock market, particularly in tech and growth stocks, has significantly impacted biotech companies, which are often seen as high-risk investments.
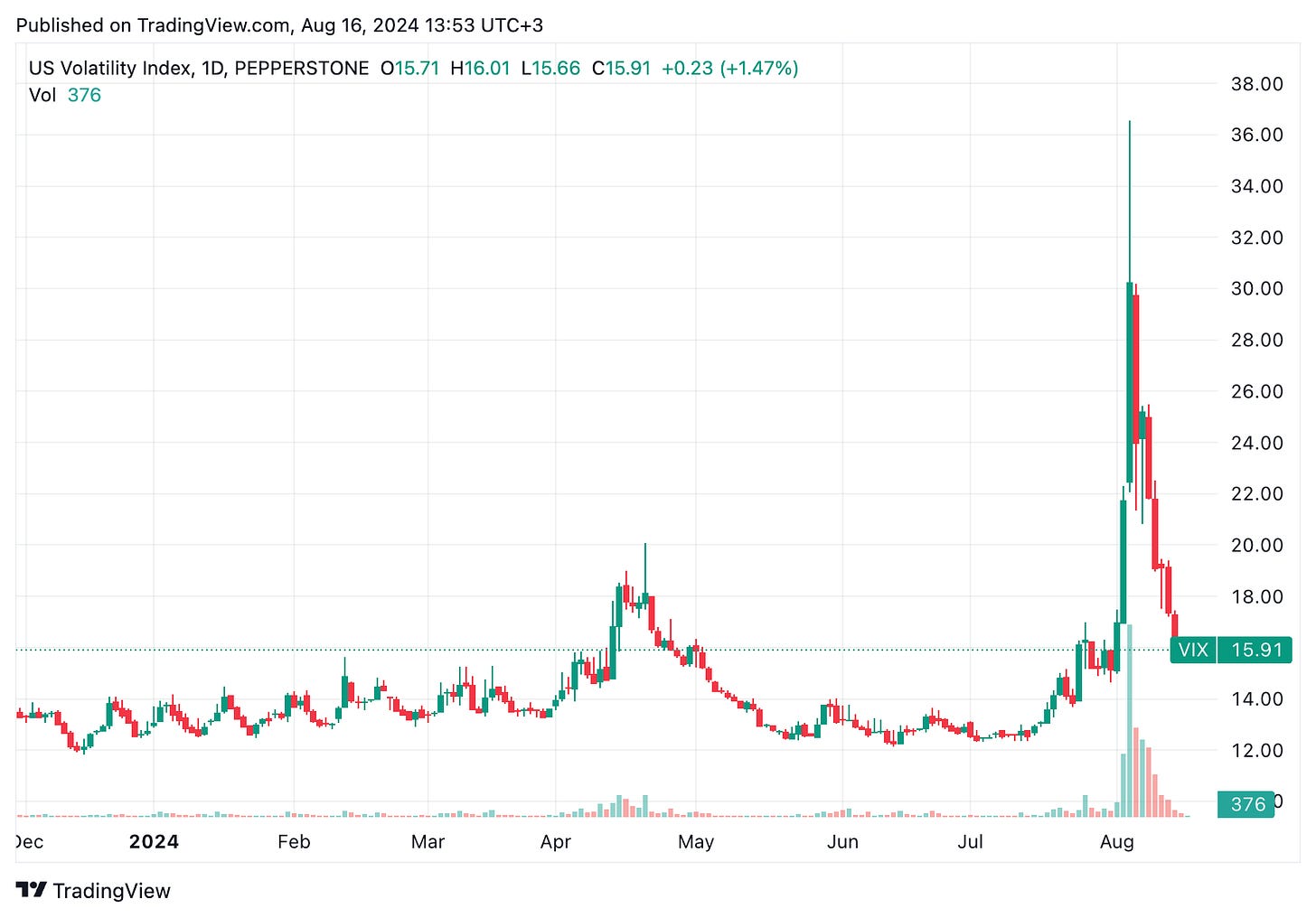
However, this was not biotech and biopharma-specific, but largely macroeconomically driven. As you can see below, the S&P500 had a large drop and has since mostly recovered.
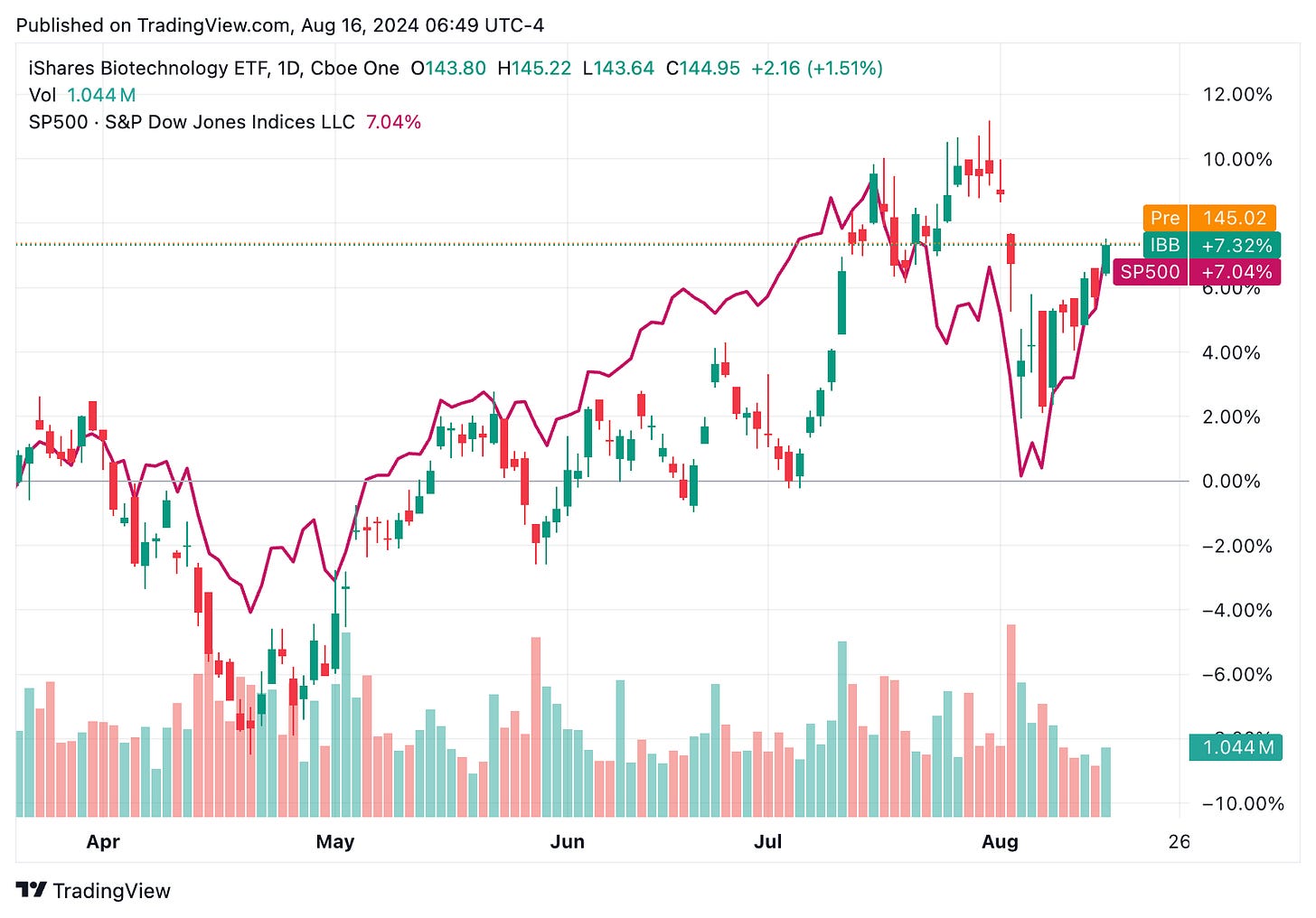
It is near impossible to know where the macro climate will take us, but with the decline in stock prices, biotech firms may face challenges in raising capital through public offerings or private investments. This could slow down research and development efforts and delay the progress of new therapies.
Despite the current challenges, there is optimism about the long-term prospects for the biotech sector, particularly as innovation continues and the demand for new therapies remains strong.
BIOTECH NEWS
🔹 Galera Therapeutics is closing down after a difficult year marked by the FDA’s rejection of its key drug candidate, avasopasem, designed to reduce severe oral mucositis in cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. The FDA’s decision, which called for a new trial, led to major layoffs and the halting of all clinical trials. Now, Galera plans to dissolve the company, reducing its workforce to just three key executives who will oversee the wind-down and potential sale of its remaining assets.
🔹 On August 14, 2024, the FDA approved Niktimvo (axatilimab) by Incyte Corporation for treating chronic graft-versus-host disease in patients who have failed at least two prior systemic therapies. The approval is based on the AGAVE-201 trial, which showed a 75% overall response rate in patients using the recommended dosage. Common side effects included elevated liver enzymes, infections, and fatigue. The drug received priority review, orphan drug, and fast track designations.
🔹 On August 14, Gilead Sciences announced that the FDA has granted accelerated approval for Livdelzi (seladelpar) for treating primary biliary cholangitis. The approval is based on data from the phase 3 RESPONSE study, where Livdelzi significantly improved biomarkers associated with liver disease progression. The FDA’s approval is contingent on ongoing confirmatory studies.
🔹 Acelyrin, a biotech company that made headlines with the largest IPO in the sector last year, is pivoting its focus away from its drug izokibep, despite promising data in autoimmune diseases like hidradenitis suppurativa and psoriatic arthritis. The company decided that these programs are better suited for a larger organization with more resources. Instead, Acelyrin will concentrate on developing lonigutamab, a drug for thyroid eye disease, which showed positive results in early studies. Additionally, Acelyrin is shelving another early-stage drug, SLRN-517, and cutting one-third of its workforce to extend its cash runway to 2027. The company will move lonigutamab directly into phase 3 testing, bypassing an earlier planned phase 2b/3 trial. This shift positions Acelyrin to compete with other companies, like Viridian Therapeutics, in the thyroid eye disease market.
🔹 Novo Nordisk has decided not to file an application in the U.S. for its once-weekly combination treatment IcoSema, which pairs insulin icodec with semaglutide, due to a recent setback with the FDA. Although the company plans to submit applications for IcoSema in other countries during the second half of 2024, the FDA issued a complete response letter for icodec, the insulin component, citing concerns related to manufacturing processes and its use in type 1 diabetes. This decision follows the FDA’s previous rejection of icodec, partially due to concerns about the risk of low blood sugar. Despite these challenges in the U.S., the IcoSema combination demonstrated superior efficacy in reducing HbA1c levels and aiding weight loss compared to insulin icodec alone in the COMBINE 1 trial. The trial also showed a lower rate of major hypoglycemia events in patients using IcoSema. The treatment was found to be safe and well tolerated overall.
🔹 Eli Lilly and Company has opened the Lilly Seaport Innovation Center (LSC) in Boston’s Seaport district, a state-of-the-art research and development facility focused on advancing genetic medicines, including RNA and DNA-based therapies. The 346,000 sq ft facility will house approximately 500 scientists and researchers, alongside 200 individuals from biotech companies within Lilly Gateway Labs, marking the first East Coast location for this innovation hub. The LSC aims to foster collaboration and accelerate the development of new treatments for diseases such as diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular conditions, neurodegeneration, and chronic pain.
🔹 On August 13, Galderma announced the FDA’s approval of Nemluvio (nemolizumab), the first monoclonal antibody targeting IL-31 cytokine signaling, for treating prurigo nodularis in adults. This chronic skin condition affects up to 181,000 people in the U.S. and is characterized by intense, persistent itching. Nemluvio received Breakthrough Therapy Designation in 2019 and Priority Review in 2024. The approval is based on successful phase 3 OLYMPIA trials, which demonstrated significant reductions in itch and skin nodules. Nemluvio is also under regulatory review in other regions, including the EU and Canada. Galderma aims to expand its use to other itch-related skin diseases.
🔹 On August 12, Stryker, a global leader in medical technologies, has announced an agreement to acquire care.ai, a company specializing in AI-assisted virtual care, smart room technology, and ambient intelligence solutions. This acquisition aims to enhance Stryker’s healthcare IT offerings and its portfolio of wirelessly connected medical devices, addressing challenges such as nursing shortages and staff retention. By integrating care.ai’s technology with Stryker’s existing platforms, the company aims to create a smart, connected ecosystem that improves clinical workflows and patient care.
🔹 On August 12, the FDA approved YORVIPATH (palopegteriparatide), the first and only treatment specifically for hypoparathyroidism in adults, a rare endocrine disorder affecting 70,000 to 90,000 people in the U.S. Developed by Ascendis Pharma, YORVIPATH is designed to provide continuous parathyroid hormone exposure through a once-daily injection. The approval is based on data from global phase 2 and 3 clinical trials. Ascendis plans to launch the drug with a support program and aims to have it available by early 2025, with possible earlier availability in late 2024. Key safety concerns include risks of hypercalcemia, hypocalcemia, potential osteosarcoma, and orthostatic hypotension.
🔹 On August 9, the FDA’s rejection of Lykos Therapeutics’ application for MDMA-assisted therapy to treat PTSD marked a significant setback for the emerging psychedelics industry. Lykos was seen as a frontrunner in integrating psychedelics into mainstream medicine, but concerns over the therapy’s safety, efficacy, and ethical conduct in clinical trials led to the decision. The FDA requested an additional phase 3 trial, emphasizing the need for more rigorous evidence. The rejection highlights the complexities of combining psychedelics with psychotherapy, a strategy that may have added to the hurdles faced by Lykos. In contrast, other companies are pivoting towards using psychedelics as standalone treatments without psychotherapy, believing this approach may streamline the approval process. Despite the setback, the broader effort to bring psychedelics into clinical use continues, with other firms refining their strategies to avoid Lykos’ pitfalls. Read more about this below.
🔹 On August 15, Lykos announced a major reorganization following the FDA’s decision. The reorganization includes 75% reduction of workforce and the appointment of Dr. David Hough, a former Janssen executive, as the senior medical advisor to oversee clinical development and FDA engagement for the resubmission. Additionally, Dr. Rick Doblin, founder of MAPS, is stepping down from the Lykos board to focus on advocacy work.
🔹 23andMe has launched a large-scale study to investigate the genetic factors influencing the effectiveness and side effects of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. Leveraging their extensive genetic database, the company aims to recruit 10,000 participants to identify genetic predictors of response to these medications, advancing the field of precision medicine.
CLINICAL TRIAL UPDATES
🔹 On August 13, top-line results from the phase 2a HuMAIN trial were published indicating that HU6, a metabolic accelerator developed by Rivus Pharmaceuticals, significantly reduces weight in patients with obesity-related heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The trial, involving 66 patients, demonstrated that HU6 met its primary endpoint of weight reduction and several secondary endpoints related to exercise capacity, quality of life, and cardiometabolic markers. HU6 is an oral, once-daily treatment aimed at weight loss while preserving muscle mass. The trial’s safety profile was favorable, and full results will be presented at the Heart Failure Society of America annual scientific meeting in September. Rivus Pharmaceuticals has also completed enrollment in a phase 2 trial for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis and plans to engage health authorities for a phase 3 study in obesity-related HFpEF in 2025.
🔹 On August 12, Pfizer announced positive top-line results from a phase 3 trial (MONeT) evaluating their RSV vaccine, ABRYSVO, in immunocompromised adults aged 18 and older. The study demonstrated that ABRYSVO was well-tolerated and generated strong neutralizing responses against RSV after a single dose. The trial included adults with conditions such as non-small cell lung cancer, end-stage renal disease, autoimmune disorders, and solid organ transplants. These findings support ABRYSVO’s potential as a protective measure against severe RSV outcomes in high-risk populations, with Pfizer planning to present these results at upcoming scientific conferences and submit them to regulatory agencies.
🔹 On August 12, the FDA has lifted the clinical hold on 4D Molecular Therapeutics’ phase 1/2 INGLAXA trial, which is evaluating the gene therapy 4D-310 for treating Fabry disease. This decision allows the company to resume patient enrollment before the end of 2024. The trial was previously paused in early 2023 after three patients experienced serious adverse events related to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. These events have since resolved, and no new significant adverse effects have been reported. Recent data from the INGLAXA trial showed promising results, with treated patients demonstrating improvements in cardiac function, exercise capacity, and quality of life, and no new significant safety concerns. The company plans to provide further updates on the program in 2025.
SCIENCE SPOTLIGHT
🔹 As mentioned in the Biotech News section, the FDA recently rejected MDMA (ecstasy) as a psychiatric treatment for PTSD, a decision that has surprised researchers and cast uncertainty on the future of psychedelic therapies. Lykos Therapeutics, the company behind the MDMA trials, plans to appeal the decision but has been asked to conduct another large-scale trial, delaying potential approval by several years.
The FDA’s concerns largely centered around the design of the clinical trials, especially the challenges of placebo control in psychedelic studies and the integration of MDMA with psychotherapy.
Additionally, on August 10, the journal Psychopharmacology retracted three MDMA-related studies due to unethical conduct at a Canadian trial site, further complicating Lykos’s efforts and highlighting ongoing issues within the field of psychedelic research.
The FDA’s decision and the controversies surrounding MDMA research could impact future applications for other psychedelics, such as psilocybin and LSD, as researchers and companies navigate the regulatory landscape and address the agency’s concerns.
Read more on this topic in my recent post:
🔹 On August 14, the WHO director general, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, declared the recent surge of mpox cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and other African countries a public health emergency of international concern. This decision follows recommendations from an independent expert committee, highlighting the rapid spread of a new strain of mpox, particularly through sexual networks in the DRC, and its detection in neighboring countries like Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda. The declaration emphasizes the urgent need for a coordinated international response to contain the outbreak. WHO is accelerating efforts to provide vaccine access, particularly in lower-income countries.
🔹 Researchers have developed an “age clock” based on the levels of 200 proteins found in the blood, which can predict a person’s risk of developing 18 chronic illnesses, including heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s. The clock’s accuracy raises the potential for a single test to evaluate the risk of various age-related conditions.
The study, led by Austin Argentieri from Mass General Hospital, used data from over 45,000 participants in the UK Biobank, significantly larger than previous studies. The clock could also accurately predict age in other diverse populations from China and Finland.
The research found that for individuals whose protein-clock age exceeded their chronological age, the risk of developing chronic diseases and conditions like frailty, slower reaction times, and premature death was higher. Conversely, the 10% of people who aged the slowest had a much lower incidence of diseases like dementia and Alzheimer’s.
🔹 A recent study published in Science Advances reveals that AlphaFold, an advanced machine learning tool, significantly outperforms traditional methods in drug discovery. Researchers in Sweden used AlphaFold to model proteins and screen over 16 million compounds to find agonists for the trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1), a target for neuropsychiatric disorders. AlphaFold models achieved a higher hit rate (60%) compared to traditional homology models (22%) in identifying potential TAAR1 ligands. One identified compound, compound 65, showed high potency and favorable pharmacokinetic properties, demonstrating strong potential for treating neuropsychiatric conditions.
Despite AlphaFold’s superior performance in some aspects, the study highlighted its limitations, particularly in predicting dynamic protein-ligand interactions and accommodating larger synthetic ligands. The research emphasizes the need for further refinement of AlphaFold and its integration with experimental data to enhance drug discovery processes.
ON THE HORIZON
🔹 August 22: In February 2024, Regeneron announced that the FDA accepted its Biologics License Application for linvoseltamab, a bispecific antibody aimed at treating relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. The application is based on positive results from the phase 1/2 LINKER-MM1 trial, which showed significant anti-tumor activity and a favorable safety profile in patients with heavily pretreated or triple-class refractory multiple myeloma. A decision from the FDA is expected by August 22, 2024.
🔹 September 5: Travere Therapeutics submitted a supplemental new drug application to the FDA earlier this year to convert the accelerated approval of FILSPARI (sparsentan) for treating IgA nephropathy (IgAN) into full approval. This submission is based on the 2-year results from the phase 3 PROTECT study, which showed significant benefits in reducing proteinuria and preserving kidney function compared to irbesartan. If accepted, the FDA will review the sNDA, with a decision expected in the second quarter of 2024. Simultaneously, the European Medicines Agency has recommended conditional marketing authorization for sparsentan in Europe, with a decision anticipated around the same time.
🔹 September 7: Avadel Pharmaceuticals initiated a phase 3 trial of LUMRYZ for idiopathic hypersomnia and is awaiting an FDA decision by September 7, 2024, on a supplemental new drug application for pediatric narcolepsy.
🔹 September 18: In December 2023, Vanda Pharmaceuticals announced that the FDA has accepted its new drug application for tradipitant, a potential new treatment for gastroparesis. The FDA’s target action date is September 18, 2024. If approved, tradipitant would be the first new drug for gastroparesis in over 40 years. The application includes data from clinical trials and non-animal preclinical studies. Gastroparesis is a condition characterized by delayed stomach emptying, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, affecting around 6 million people in the U.S. The NDA submission includes safety data from over 1,000 patients and highlights Vanda’s push for alternative toxicity testing methods.
🔹 September 21: In March, Zevra Therapeutics announced that the FDA has extended the review period for its new drug application for arimoclomol, a treatment for Niemann-Pick disease type C. The new PDUFA action date is September 21, 2024.
🔹 September 25: The FDA has granted Priority Review to Merck’s supplemental Biologics License Application for KEYTRUDA combined with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic malignant pleural mesothelioma. The application is based on positive results from the phase 2/3 CCTG IND.227/KEYNOTE-483 trial, which showed that KEYTRUDA plus chemotherapy significantly improved overall survival, progression-free survival, and objective response rates compared to chemotherapy alone. The FDA’s decision is expected by September 25, 2024.
🔹 September 26: Bristol Myers Squibb is anticipating a crucial FDA decision by September 26, 2024, on KarXT (xanomeline-trospium), a novel antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenia. Acquired through BMS’s March 2024 purchase of Karuna Therapeutics, KarXT represents the first new drug class for schizophrenia in several decades, offering a unique mechanism that targets muscarinic acetylcholine receptors instead of dopamine receptors. Clinical trials have shown promising results, with significant improvements in schizophrenia symptoms. If approved, KarXT could be a groundbreaking treatment in the field, with potential applications in other conditions like Alzheimer’s and Bipolar I disorder.
🔹 September 27: The FDA has granted Priority Review to Sanofi’s Sarclisa (isatuximab) for use in combination with standard-of-care treatment (bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone, or VRd) for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients who are ineligible for transplant. This decision is based on positive results from the phase 3 IMROZ study, which showed significant improvement in progression-free survival when Sarclisa was added to VRd compared to VRd alone. If approved, Sarclisa would become the first anti-CD38 therapy available for this patient group, marking its third indication for multiple myeloma. The FDA is expected to make a decision by September 27, 2024. Results from the IMROZ study will be presented at major medical conferences later in the year.
Happy Friday, thanks for reading and have a great weekend!
DISCLAIMER: This content is for informational purposes only. It should not be taken as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice. The views expressed here are my own and do not reflect the opinions of any company or institution.
DISCLOSURE: I have no business relationships with any company mentioned in this article.



